Required minimum distributions
The RMD tool allows advisors to highlight the best options for generally middle market clients nearing or currently in their retirement years.
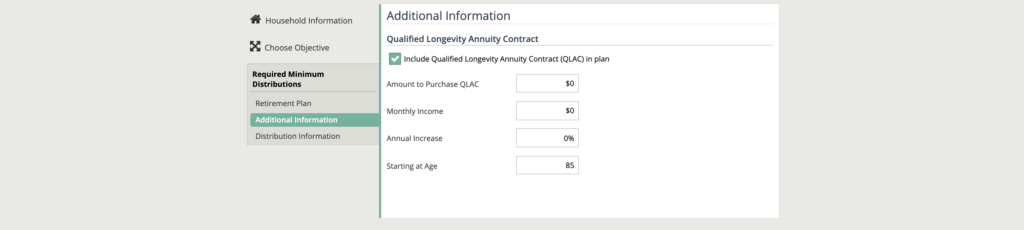
Additional information
After filing out the Retirement Plan tab for the Required Minimum Distributions objective, the option to select a Qualified Longevity Annuity Contract is available.
A QLAC is a deferred annuity that is funded by your client’s investments sourced from a qualified plan or IRA.
Distribution assumptions
At the top of the Distribution Information tab under the Required Minimum Distribution objective is an option to select if your client qualifies to delay distributions past age 72. In order to qualify for this the client must remain actively employed AND own less than 5% of the Plan Sponsor (business or employer) or their Plan is a 403(b) plan that is not a government or church plan.
The distribution method options include the
- Safe Harbor Method under IRC Sec. 72(t)
- Distribute an annual distribution
- Scheduled distribution
Single vs. Uniform Lifetime Table
The uniform distribution table is the life expectancy table to be used by all IRA owners to calculate lifetime distributions unless your beneficiary is your spouse who is more than 10 years younger than you.
The single life expectancy table is based on the age after the IRA owner’s death. That factor is reduced by one for each succeeding distribution year.
Many people are opposed to paying the penalty tax for early distributions and ask the question, “Is there a way to avoid it?” Yes, there is: the Safe Harbor distribution methods. Following the rules of the Safe Harbor distribution methods is one of the exceptions for the 10% early distribution penalty. There are three methods that qualify as a Safe Harbor method:
- Life expectancy method is calculated the same way as Required Minimum Distributions (RMD), but it simply starts at a younger age. It’s a variable annual payment that fluctuates with the account balance each year. It is usually the smallest initial annual payment and the annual payment may increase or decrease if the account earns more (or less) interest than assumed in the projected calculations.
- Amortization Method is a level annual payment amortized over life expectancy that, once calculated, the distribution remains the same each year. It is usually a lower annual payment and slower spend-down of the account, and there are more choices for life expectancy calculation.
- Annuity Method is very similar to the amortization method but it uses a level annual payment based on the life only annuity tables. It is usually the highest annual payment and fastest spend-down of the account. It is the least flexible method.
